Know how physiotherapy supports both mobility and mental health in seniors
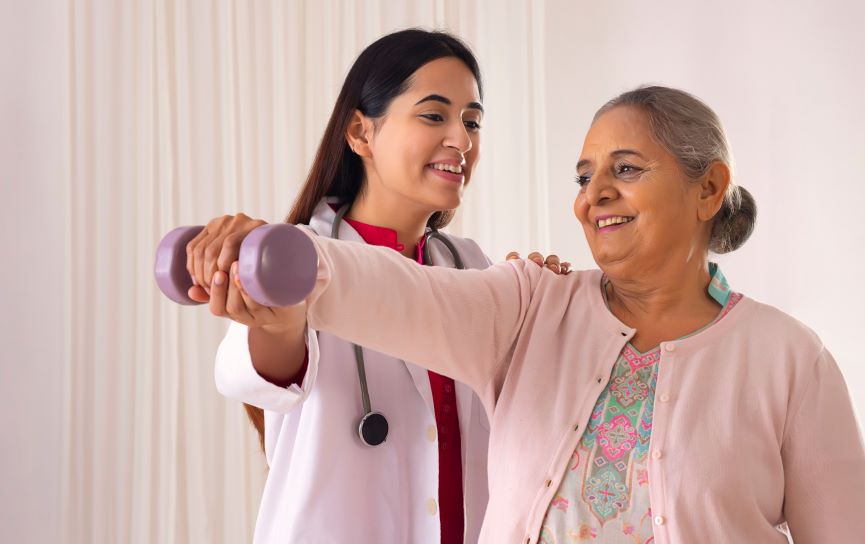


Know how physiotherapy supports both mobility and mental health in seniors

Geriatric Senior Counseling

What are the benefits of going to a geriatric specialist?

What’s the difference between a geriatrician and a gerontologist?
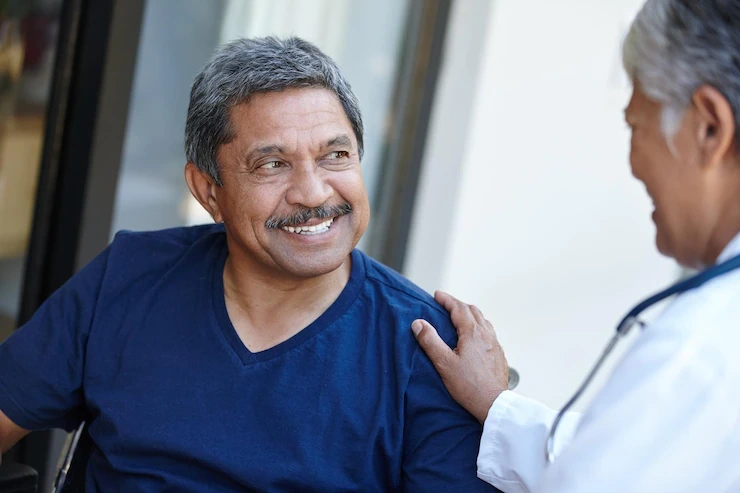


Top 4 strategies to encourage and support your elderly loved ones healthy habits

Safeguarding Seniors: Understanding and Preventing Falls with Dr. NN Prem

My Personal Caregiving Journey for My Parents.

Polypharmacy as a burden among Indian patients
Senior Citizens: They need to be careful about risks of polypharmacy
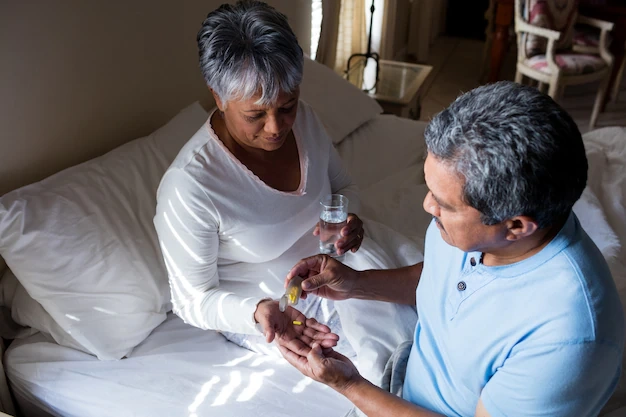

When to Refuse Antibiotics for Infections

The Pros and Cons of Living in an Old Age Home