Atherosclerosis: Symptoms Cause and Prevention
01-10-24
What is atherosclerosis?
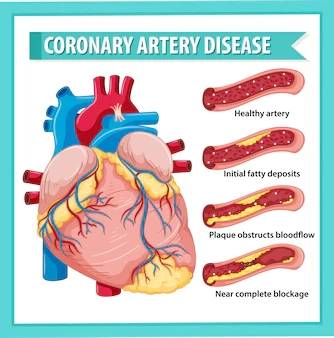
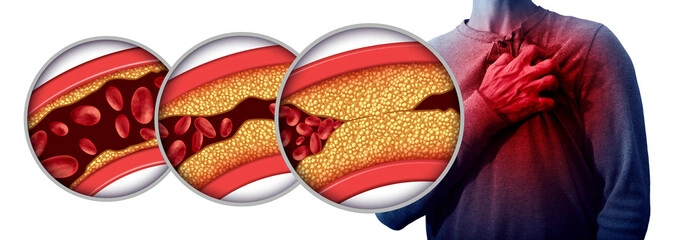
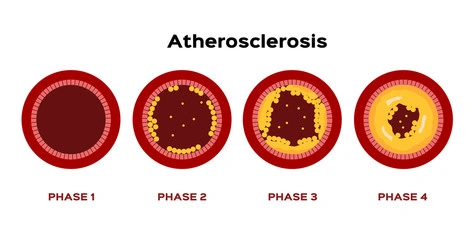
Atherosclerosis is a condition in which the blood vessels are narrowed due to the build-up of plaque. Blood channels called arteries transport oxygen-rich blood to your heart and other body components.
Plaque is made up of cholesterol, calcium, and other elements in the blood. Plaque hardens and narrows arteries over time. As a result, less oxygen-rich blood can reach your body's organs and other tissues.
Typically, atherosclerosis doesn't produce symptoms until an artery is either completely blocked or significantly narrowed. The disease is frequently unknown to many people until they experience a medical emergency, like a heart attack or stroke.
What are the symptoms of atherosclerosis?
Some persons may exhibit the disease's symptoms and indicators. Which arteries are impacted will determine the signs and symptoms.
Coronary arteries
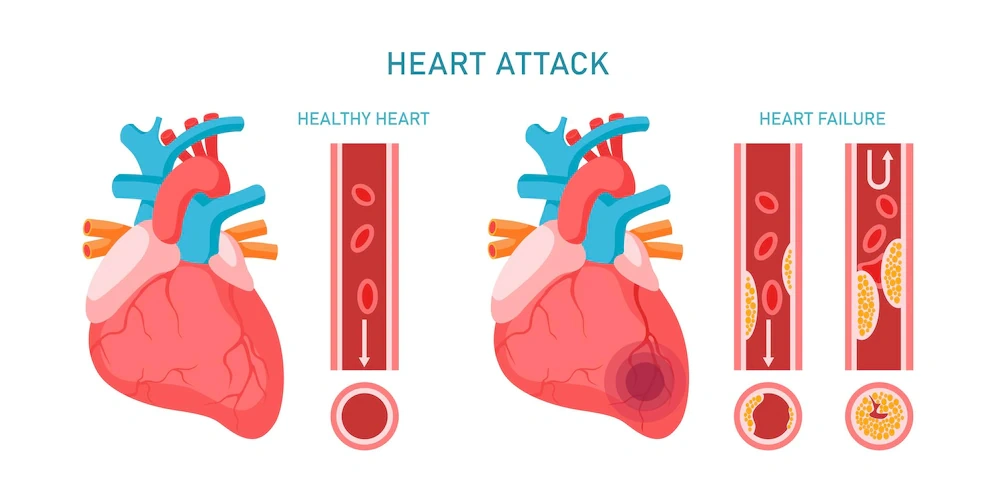
The coronary arteries supply the heart's oxygen-rich blood.
●Angina may develop if plaque restricts or plugs these arteries (a condition known as coronary heart disease, or CHD).
●Chest tightness
●The shoulders, arms, neck, jaw, or back may all experience pain.
●Arrhythmias and shortness of breath are other signs of CHD.
●Shortness of breath
●Fatigue
●Sleep problems
Carotid arteries
These arteries supply blood to our brain cells. Blockage of these arteries may cause the following symptoms:
●Sudden weakness
●Numbness or paralysis of the face, arms, or legs, particularly on one side of the body
●Confusion
●Difficulty comprehending or speaking
●Difficulty with vision in one or both eyes
●Having trouble breathing
●Unexpected falls, balance or coordination issues, difficulty walking, and dizziness
●Loss of consciousness
●Abrupt and severe headache
Peripheral arteries
Major arteries that supply the legs, arms, and pelvis with oxygen-rich blood can also develop plaque (a disease called peripheral artery disease). This may cause
●Numbness
●Pain
●Infections
Renal arteries
The kidneys receive oxygen-rich blood from the renal arteries. One may develop chronic kidney disease if plaque accumulates in these arteries. The chronic renal disease gradually reduces kidney function over time. Early kidney disease frequently has neither symptoms nor indicators. As the condition worsens, it can lead to:
●Fatigue
●Changes in urination (more or less frequently)
●Lack of appetite
●Nausea
●Swelling of the hands or feet
●Itching or numbness
●Trouble sleeping
What are the causes of atherosclerosis?
The cause is unknown. Atherosclerosis, however, is a slow, complicated disease that can begin in childhood, according to research. With age, it develops more quickly.
Atherosclerosis may develop when specific factors damage the inner layers of the arteries. These factors may include:
●Smoking
●High blood cholesterol and specific fat levels
●Elevated blood pressure
●High blood sugar levels brought on either diabetes or insulin resistance
How can you prevent it?
By taking steps to manage risk factors, atherosclerosis and related disorders can be avoided or delayed. The more risk factors you have, the higher your risk for developing atherosclerosis is.
If you have atherosclerosis, your doctor may advise both medication counsel and adjustments to your lifestyle that are good for your heart. A healthy weight, regular exercise, stress management, and giving up smoking are all examples of heart-healthy lifestyle modifications.
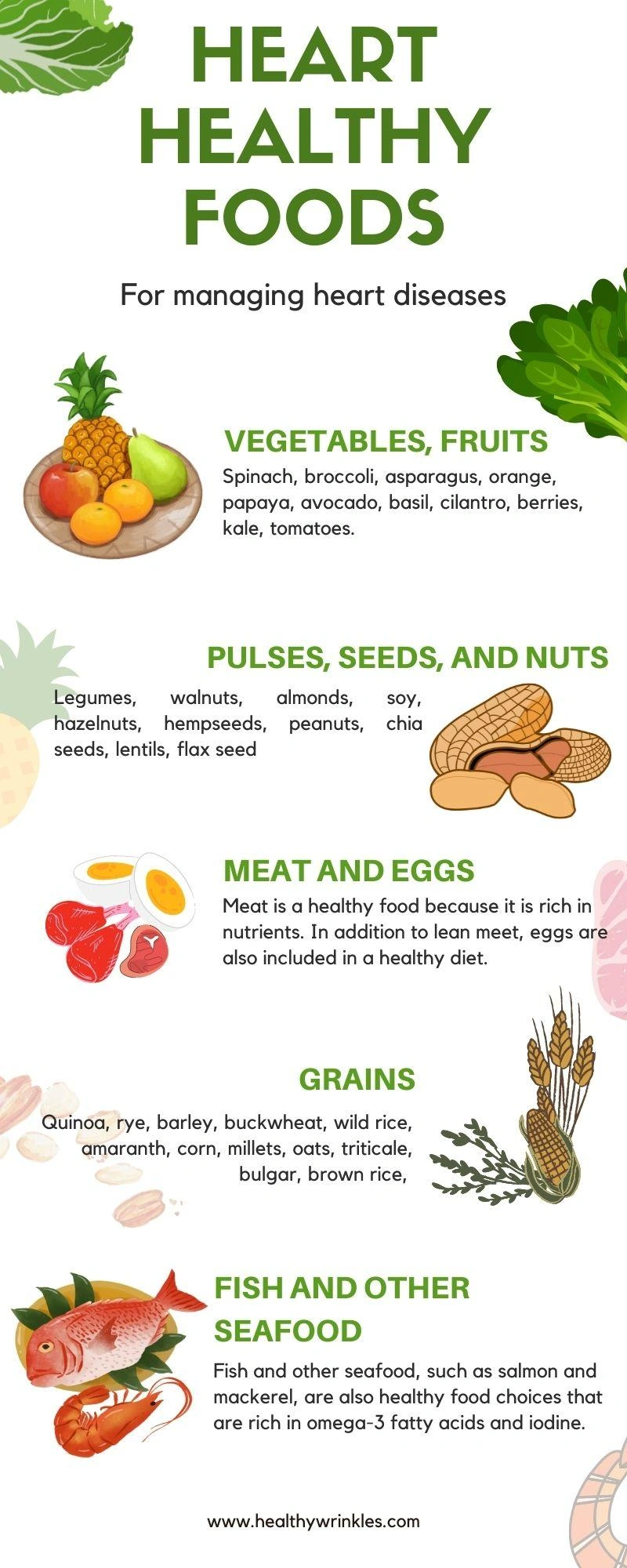
Eating Heart-Healthy
Eating heart-healthy foods may lower your chances of getting affected by atherosclerosis.
●Dairy items that are fat-free or low in fat, such as skim milk
●Eat fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids such as salmon, tuna, and trout approximately twice a week
●Fruits like pears, apples, bananas, oranges, and prunes
●Legumes such as beans, kidney beans, lentils, black-eyed peas, and chickpeas
●Vegetables including carrots, broccoli, and cabbage
●Wholesome grains, like oats, corn
Controlling Stress
Emotional and physical health can be enhanced by learning how to control stress, unwind, and deal with challenges. Take into account beneficial stress-reduction exercises like:
●Stress management programs
●Meditation
●Physical exercise
●relaxation training
●Having a discussion with family or friends
Physical exercise
Numerous atherosclerosis risk factors, such as LDL or "bad" cholesterol, high blood pressure, and excess weight, can be reduced by engaging in regular physical exercise. Additionally, exercise can increase HDL or "good" cholesterol, which helps avoid atherosclerosis, and lower diabetes risk.
Avoid smoking
Quit smoking and using tobacco if you do. Smoking can harm blood arteries, tighten them, and increase the risk of atherosclerosis. Consult your doctor for information on goods and programs that assist with stopping. Try to prevent passive smoking as well.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
In addition to improving general health, maintaining a healthy weight helps reduce the risk of developing coronary heart disease. Knowing your body mass index (BMI) can help you determine a healthy weight for your height, and provide a rough approximation of your total body fat. The normal range is 18.5-22.9