Does this actually happen to our skin as we age?
01-10-24
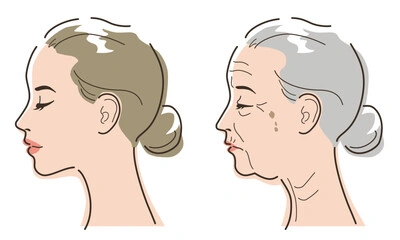
Our skin experiences various changes as we age, making it more brittle and vulnerable to damage. Let's examine some of these aging-related skin changes in more detail and how they impact wound healing.
Thinning of skin layers
The inner and outer layers of the skin together are in charge of controlling body temperature, safeguarding the body from harm, and acting as a barrier against environmental factors.
These layers get thinner and thinner over time. Because of the reduced surface area for nutrition transfer, oxygen and nutrients cannot travel as effectively through the skin layers.
To prevent tears and cuts to the skin, you can choose clothes with full sleeves and long pants.
Decreased cell turnover rate
Older cells are regularly replaced by new ones as they rise upward from the skin's base to the surface. The rate of this cell turnover mechanism decreases as we age. Therefore, any skin damage or injury in an older person takes longer to heal. Retinols and vitamin C products can help in increasing the cell turn over rate.
Decrease in connective tissue components
The alterations in connective tissue components such as elastin, collagen, and others are one of the main elements in the formation of wrinkles in older people. Reduced oil production in aging skin lowers skin hydration, which can lead to issues like dry skin and irritation.
Sweat glands, which are crucial for cell regeneration and controlling body temperature, may function differently with age. We can improve our skin by using agents that contain collagen, essential fatty acids, hyaluronic acid, and other essential minerals.
Increase in capillary fragility
Small blood tubes called capillaries link the venous and arterial systems. They make it easier for nutrients and waste materials to move back and forth between veins and arteries. With aging, the capillary walls become thin and brittle, which leads to the frequent easy bruising that older people experience.
When the capillaries are broken or damaged, they can't efficiently transport waste and debris from the wound tissue or oxygen and nutrients to the tissue. Additionally, aging decreases the development of new blood vessels, which may indirectly affect how quickly a wound heals.
Vitamin C and tools that promote effective blood circulation may help with this issue in the elders.
The inflammatory response is delayed
An instinctive immune response known as the inflammatory response typically begins right away after an injury. However, studies suggest that aging may have an impact on how the inflammatory response is triggered and controlled. Inflammation can therefore last longer than usual and potentially develop into a chronic problem. As a result, wounds take longer to heal and are more likely to develop problems. Retinoids, immune therapies, and other therapies may help in fastening the inflammatory response in seniors.
Age-related changes can affect how quickly a wound heals, so it's crucial for older people to take precautions to avoid getting hurt.